There are certain patterns that relationships tend to take over time in regards to overall happiness and satisfaction. In order to truly understand your relationship, it’s best to take a broader view, rather than examine a small slice of time that may not be representative of the whole. Which of the following patterns do you relate to?
The Idealized Relationship
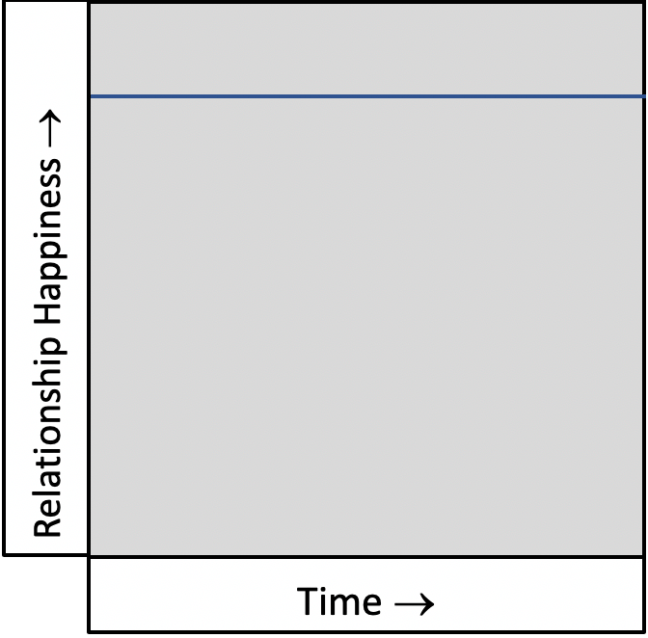
This is the relationship that Hollywood tells us to expect. We are conditioned to believe that once we find “the one,” the relationship will be easy and happiness will be guaranteed and omnipresent.
The Volatile Relationship
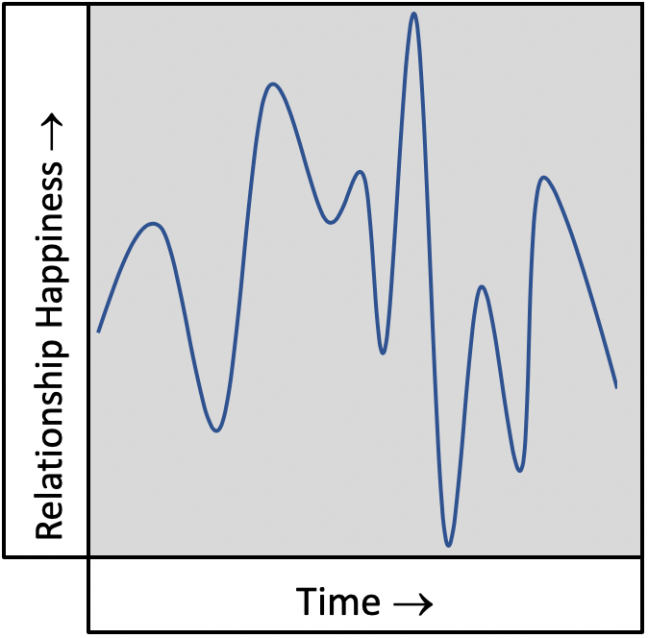
This pattern can be addictive because when it’s good, it’s REALLY good. On the other hand, when it’s bad, it’s horrid. The highs keep you in it and hope that it will smooth out keeps you from leaving.
The What Goes Up Must Come Down Relationship

This is the relationship that is on fire in the beginning and then settles down into a more sedate happiness and contentment over time. It’s far from bad, but the partners may find themselves craving the intensity of the beginning.
The Slowly Declining Relationship
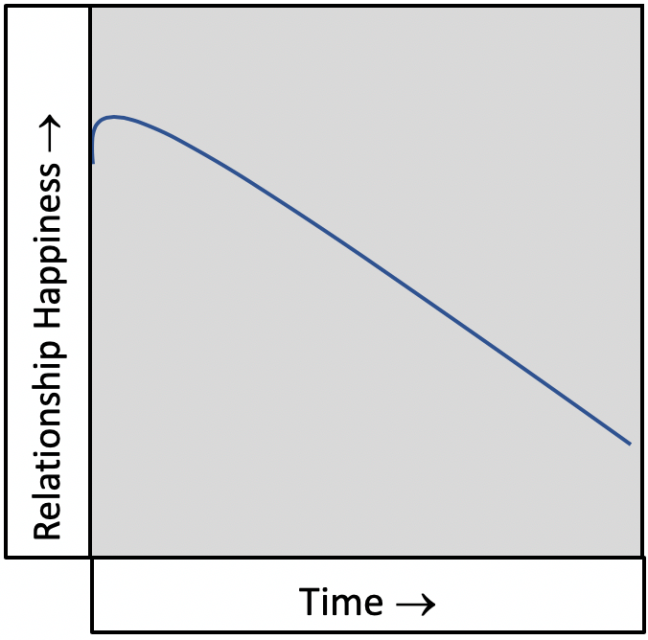
It WAS good, but it seems to be trending further and further away from that place. The connection is waning and you may feel like you love them, but you’re no longer “in love” with them.
The Gradually Improving Relationship
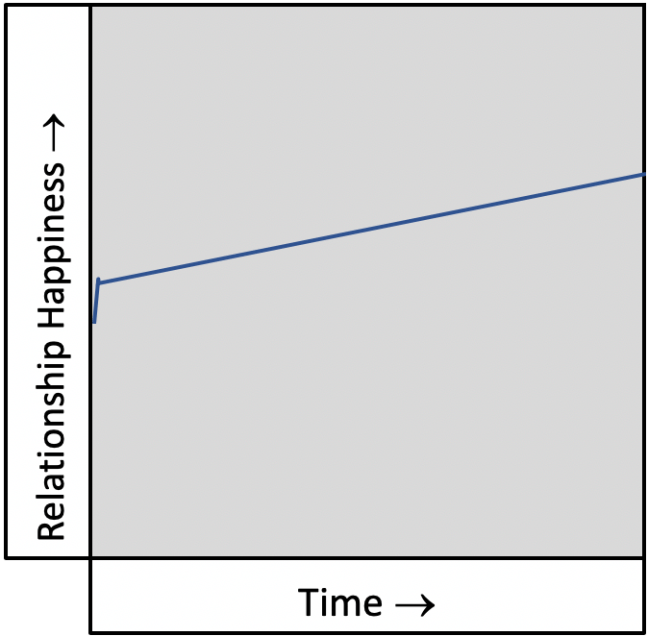
This is the relationship between two people that are growing together. Over time, they have learned to temper their expectations and to accept the other as they are.
The Devil You Know Relationship

It’s not good, but for now, it’s better than being alone. Strangely, the consistency of this relationship can be comforting; you know exactly what to expect.
The Life is a Highway Relationship

This is different from the volatile pattern because the ups and downs are less extreme and balance each other out. This is the marriage that is happy overall with some good days and some not-so-good ones.




